How do Phragmites Spread?
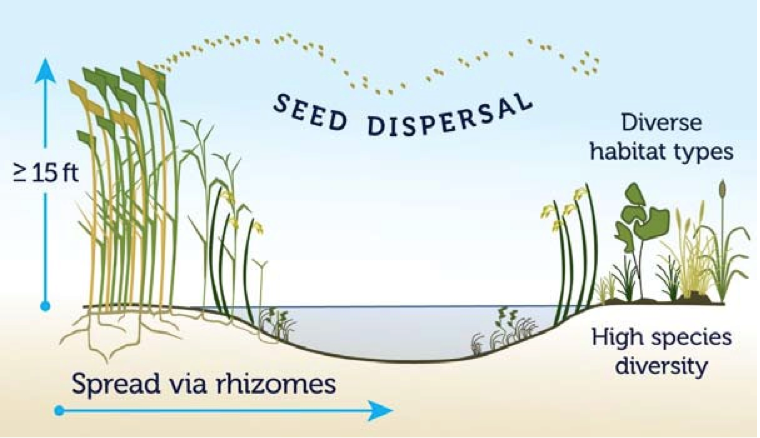
- Predominantly through seed dispersal. (Each Phragmites produces up to 2,000 seeds per year.)
- Stolons expand around an area where the plant is already established. (Stolons are stems that are connected to the parent plant that grow along the soil surface and can form roots and shoots.)
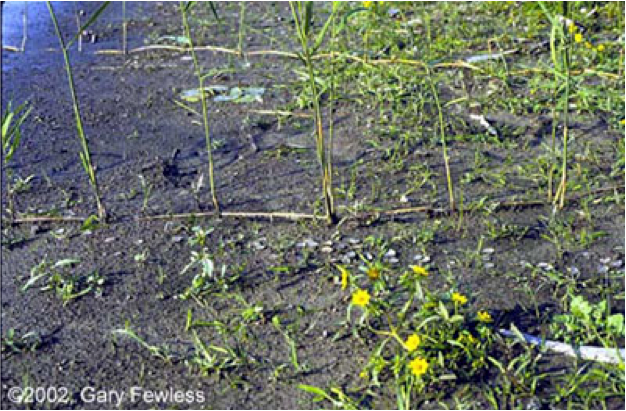
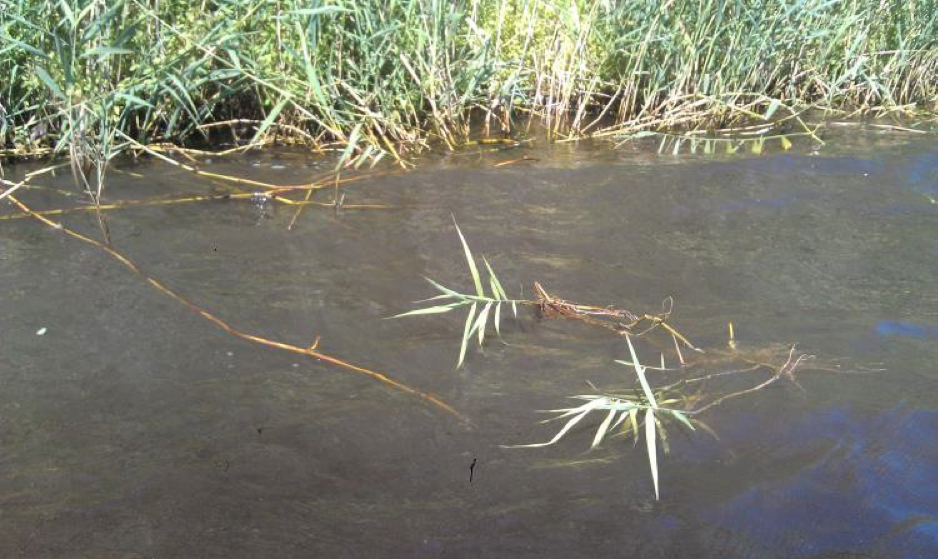


- Rhizomes also expand around an area where the plant is already established. (Rhizomes are underground stems connected to the parent plant that are capable of growing roots and shoots.)
- Rhizomes are the means by which phragmites spread into the lakes and water system. This is a critical issue, because once they establish themselves in water there are no means for eradication.
- Pieces of rhizomes or stolons are broken off of a parent plant by natural forces such as wind or flood waters, and are moved to a new location where they can root.
- Humans more them purposefully or accidentally i.e. construction equipment that was not properly cleaned.
- Humans unintentionally plant it as a garden ornamental, use it for floral displays, or as camouflage for duck blinds.


